ANSED/KANE-EGA1|CAB Single Exhaust Gas Analyzers – CO2
It is important that you register your new ANSED products within 30 days after purchase in order to activate the warranty. Fill in the form
Overview:
- Single Exhaust Gas Analyzers – CO2 For Auxiliary Power Units (APU) & In-Cab Heaters
Key Features:
- Measures CO2, 0-20%.
- Rechargeable NiMH AA long-life batteries, supplied with USB1 charger.
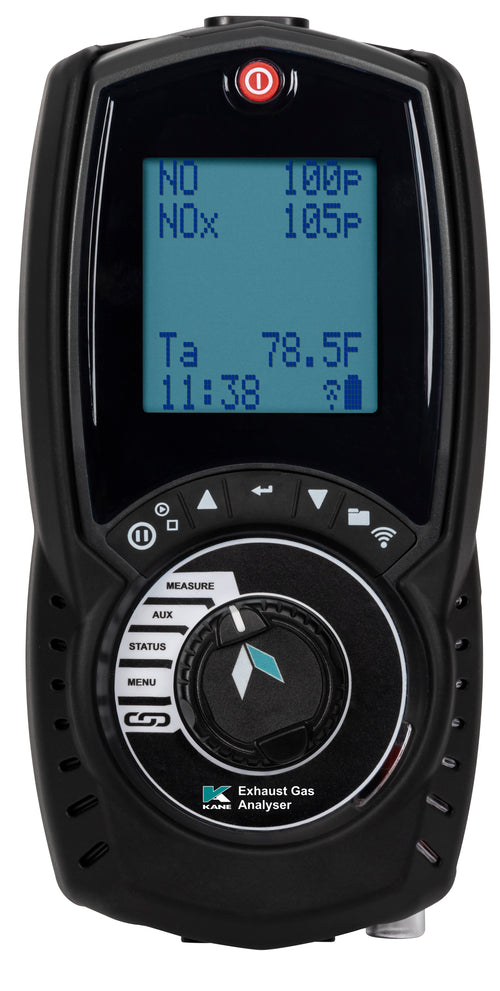
- Illuminated display (7.5cm/3” diagonal) with rotary dial & 6-line display for ease of use.
- Connect to KANE LIVE APP, free with kit
- Store up to 45 tests.
- Compact & rugged with a protective rubber sleeve & magnets for hands-free operation.
- Integrated water trap with replaceable particle filter.
- Document test results with optional KANE-IRP3 printer.
In the ANSED/KANE-EGA1CAB Kit:
- KANE-EGA1 CO2 handheld gas analyzer – weighs 0.625kg (1.38 lbs)
- EP5 probe (O.D. 6mm) – length 4m (13.1ft)
- USB1 &AC charger
- User Manual
- KANE LIVE APP
- Carry bag
- Downloads
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Please refer to the Resource Center for Important Downloads.
What is NOx?
NOx (nitrogen oxides) forms when high combustion temperatures cause nitrogen from the air to combine with oxygen. Diesel engines produce higher NOx levels than gasoline engines due to their combustion process.
NOx is a regulated air pollutant, monitored by the EPA.
How do modern diesel engines reduce NOx emissions?
They use several systems:
-
EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) – reduces combustion temperature.
-
SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) – chemically reduces NOx.
-
DEF/AdBlue Injection – provides urea for NOx conversion.
What is AdBlue/DEF and how does it reduce NOx?
-
AdBlue/DEF is an additive (urea solution) injected into the SCR catalyst.
-
Inside the SCR, urea converts into ammonia.
-
Ammonia reacts with NOx and lowers emissions.
-
The amount injected depends on data from the vehicle’s NOx sensors.
Why is tailpipe NOx testing important?
Because SCR-mounted NOx sensors cannot distinguish between NOx and ammonia, they may report ammonia as NOx. This can cause incorrect DEF dosing.
A NOx gas analyzer (like the KANE-EGA1NO) is the only accurate method to verify actual processed NOx at the tailpipe.
What types of trouble codes can tailpipe NOx testing help diagnose?
DEF / AdBlue System Codes:
-
P20EE and multiple SPN codes
SCR & emissions codes:
-
P0401, P0420, P0440
-
P2459, P2002
When should I use a NOx analyzer in diagnostics?
Use it when:
-
Scan tool data is inconclusive
-
NOx sensors could be faulty
-
DEF injection might be incorrect
-
The SCR may not be reducing NOx properly
A NOx analyzer validates the true emissions performance of the DEF/SCR system.
What must be verified before performing tailpipe NOx testing?
Use your scan tool to confirm:
-
No underlying engine-related issues
-
Engine-out NOx is within expected range
If engine-out NOx is excessive, the SCR cannot achieve proper reduction.
How do I compare scan-tool NOx sensor values with the KANE-EGA1NO analyzer?
-
Connect the scan tool.
-
Measure tailpipe NOx with the EGA1NO.
-
Compare values:
-
If readings align, sensors are functioning properly.
-
If they differ, a sensor fault is likely.
-
What is the correct procedure for road-testing with the KANE-EGA1NO?
-
Connect the scan tool and NOx analyzer.
-
Disconnect the DEF/AdBlue injector.
-
Drive until ammonia in the SCR is depleted.
-
Warm up the NOx sensor (~20 minutes).
-
In steady state, NOx Sensor 1, NOx Sensor 2, and tailpipe NOx should match.
How do I identify a faulty NOx sensor?
During the steady-state road test:
-
If either NOx sensor does not match the analyzer’s tailpipe reading → faulty sensor.
What do I do after verifying the sensors?
-
Reconnect the DEF/AdBlue injector.
-
Clear codes.
-
Perform another road test.
-
Check reduction levels.
What is considered a proper NOx reduction level?
A correctly operating system should show ~90% NOx reduction at the tailpipe after the DEF/SCR system is active.
What does it mean if there is no NOx reduction?
Likely issues include:
-
DEF/AdBlue injector malfunction
-
Crystallized DEF deposits
-
SCR catalyst problems
-
Sensor faults (if not already ruled out)
Why can NOx sensors give false high readings?
Because they cannot differentiate between NOx and ammonia, excess DEF injection can cause ammonia slip, leading the sensor to falsely report high NOx levels.
A tailpipe analyzer is needed to confirm true NOx.
What does the NOx pass/fail guide indicate?
It provides reference levels showing whether the SCR is reducing NOx effectively.
(From the document: PASS ≈ 90% reduction; FAIL = little or no reduction.)
What safety considerations apply during this testing?
Road tests must be performed:
-
Safely
-
By qualified personnel
-
In a roadworthy vehicle
ANSED is not responsible for damages, expenses, or loss of earnings.
What are the key features of the KANE-EGA1NO analyzer?
-
Handheld & portable
-
Fast warm-up (≈90 seconds)
-
Stores/prints diagnostic reports
-
Pre-/Post-repair comparisons
-
Water trap & particulate filter
-
Works with diesel, gasoline, LPG, CNG
-
Bluetooth connection with KANE LIVE app
How does the KANE-EGA1NO save money in diesel diagnostics?
It prevents misdiagnosis by identifying sensor faults, SCR malfunctions, or DEF injector issues before expensive parts are replaced.
Shops can avoid:
-
Unnecessary parts costs
-
Unbillable labor
-
Repeat repairs
California residents: Proposition 65 Information This product may contain chemicals, including lead, which are known to the State of California to cause cancer and birth defects or other reproductive harm. Read more